Boundary Loss for Remote Sensing Imagery Semantic Segmentation
1Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Aeronet group2Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, ADASE group
International Symposium on Neural Networks 2019
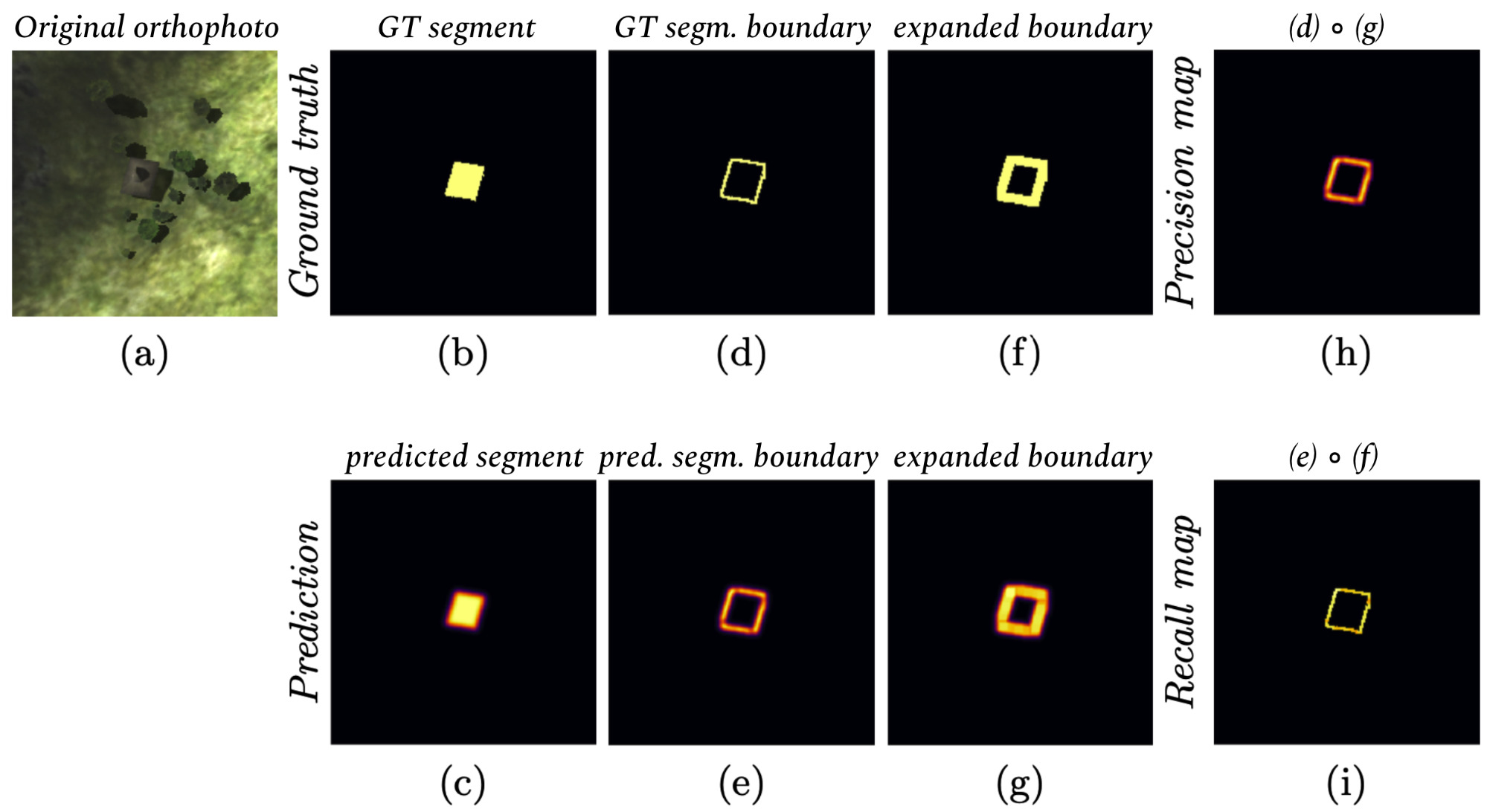
(a) original orthophoto; (b) ground truth segment (gt); (c) predicted segment (pred); (d) boundary of gt; (e) boundary of pred; (f) expanded boundary of gt; (g) expanded boundary of pred; (h) pixel-wise multiplication of masks (d) and (g); (i) pixel-wise multiplication of masks (e) and (f)
Abstract
In response to the growing importance of geospatial data, its analysis including semantic segmentation becomes an increasingly popular task in computer vision today. Convolutional neural networks are powerful visual models that yield hierarchies of features and practitioners widely use them to process remote sensing data. When performing remote sensing image segmentation, multiple instances of one class with precisely defined boundaries are often the case, and it is crucial to extract those boundaries accurately. The accuracy of segments boundaries delineation influences the quality of the whole segmented areas explicitly. However, widely-used segmentation loss functions such as BCE, IoU loss or Dice loss do not penalize misalignment of boundaries sufficiently. In this paper, we propose a novel loss function, namely a differentiable surrogate of a metric accounting accuracy of boundary detection. We can use the loss function with any neural network for binary segmentation. We performed validation of our loss function with various modifications of UNet on a synthetic dataset, as well as using real-world data (ISPRS Potsdam, INRIA AIL). Trained with the proposed loss function, models outperform baseline methods in terms of IoU score.Materials
Contact
If you have any questions about this work, please contact us under adase-3ddl@skoltech.ru.